

A higher point total provides evidence that the message may be spam when there's sufficient evidence, the filter rejects the null, classifying the message as junk. The inverse square law proposed by Newton suggests that the force of gravity acting between any two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the. The null hypothesis is that the e-mail is a real message and should go to your inbox. Discover the factors that affect gravitational attraction, and determine how adjusting these factors will change the gravitational force. We can think of the filter's decision as a hypothesis test. Visualize the gravitational force that two objects exert on each other. The center of attraction (the sun, for instance, in the case of a planet’s or comet’s orbit) is at the point O. The semimajor axis is a, the semiminor axis is b, and the eccentricity e 1 b2 / a2 0.745 in this case. The filter has a cutoff value for the point total any message rated lower than that cutoff passes through to your inbox, and the rest, suspected to be spam, are diverted to the junk mailbox. I have drawn one such ellipse for you in Figure 10.1.3. The higher the point total, the more probable it is that the message is unwanted. The filter reads each incoming e-mail and assigns points to the sender, the subject, keywords in the message, and so on. The signal is detected by a supercon-ducting differential accelerometer, making a highly sensitive sensor of the gravity force generated by the source mass.Spam filters try to sort your e-mails and decisive which are real messages and which are unwanted.
Two test masses, also disk-shaped, are suspended on the two sides of the source mass at a distance of 100 μm to 1 mm. This animation, originally created for a KET Distance Learning physics course, explains the mathematical formula for the 'Inverse Square Law' by. To minimize Newtonian errors, ISLES employs a near-null source of gravity, a circular disk of large diameter-to-thickness ratio.
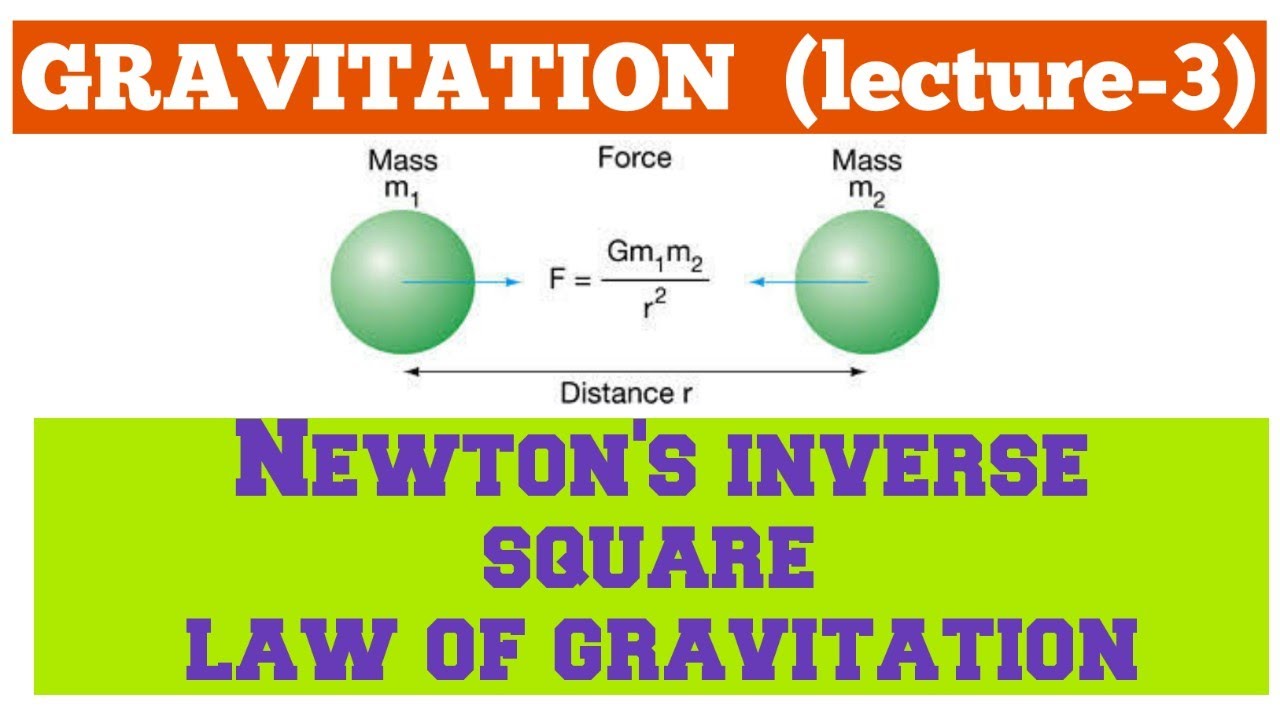
The low-damping magnetic levitation, combined with a low-noise SQUID, leads to extremely low intrinsic noise in the detector. The direction of the force is along the line joining the centers of the. In SI units, the constant k has the value k 8.99 × 10 9 N m 2 /C 2. The constant of proportionality k is called Coulomb’s constant. Brightness of light and loudness of sound. How strong is the Suns gravitational pull on the Voyager 1 spacecraft now as compared to when it was at Jupiter How much pull does the Sun exert on the. This equation is known as Coulomb’s law, and it describes the electrostatic force between charged objects. 4 times weaker (according to inverse square law) zero. As designed, the experiment will be cooled to less than 2 K in NASA’s low temperature facility the LTMPF, allowing superconducting magnetic levitation in microgravity to obtain very soft, low-loss suspension of the test masses. Terms in this set (27) The force of gravity between two objects gets weaker with the square of the distance. Some parameters of several torsion balances designed for gravity measurements are summarized in Table 1, and compared to the balance used in the present. The measures to be applied for reducing the effects of disturbances will be described in this presentation. To accomplish these goals on the rather noisy International Space Station, the experiment is set up to provide immunity from the vibrations and other common-mode accelerations. ISLES will be sensitive enough to detect axions with the strongest allowed coupling and to test the string-theory prediction with R⩾5 μ m. only within the last century that any laboratory experiments have been made to test the inverse square law for gravitation, and all but one has been carried. The objective of ISLES (inverse-square law experiment in space) is to perform a null test of Newton’s law on the ISS with a resolution of one part in 10 5 at ranges from 100 μm to 1 mm. Law of universal gravitation and inverse square law For any two objects, the force of attraction is proportional to the mass of each object.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
